HT5. Everything You Need to Know About Gen*tal Herpes
Have you recently discovered a bump, spot, or unusual lesion in your intimate area and are unsure what it means? You’re not alone—and it’s completely normal to feel concerned. While some skin changes may be harmless, others could indicate conditions that require medical attention.
In this article, we’ll help you better understand common causes of genital skin changes, how to recognize warning signs, and when it’s important to speak to a healthcare provider.
What Causes Genital Bumps or Skin Changes?
There are several possible reasons for bumps or lesions in the genital area. Some are temporary and related to daily habits, while others may be signs of an underlying medical condition. Here’s a breakdown of the most common explanations:
1. Folliculitis
This occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, often after shaving or wearing tight clothing.
What it looks like: Small red or white bumps that may feel itchy or tender. Sometimes, they contain pus.
What to do: Keep the area clean, avoid further irritation, and apply a warm compress. If the bumps worsen or don’t improve, see a healthcare provider.
2. Sebaceous Cysts
These are noncancerous lumps caused by blocked glands beneath the skin.
What it looks like: Smooth, flesh-toned or yellowish bumps that are usually painless unless infected.
What to do: They often go away on their own. If they become painful or swollen, medical drainage may be needed.
Conditions That May Require Medical Evaluation
While some causes of bumps are benign, others may indicate infections or skin conditions. Below are some examples that should be evaluated by a healthcare provider:
Genital Warts
-
Caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
-
Typically appear as small, flesh-colored growths, sometimes in clusters.
-
Often painless but may cause mild irritation.
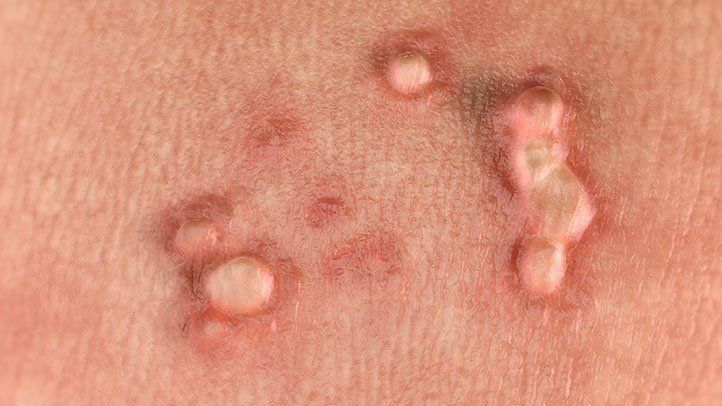
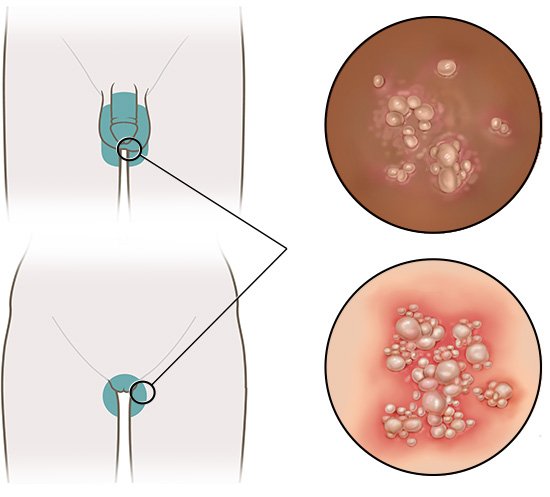
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
-
Can cause painful blisters or open sores in the genital area.
-
Symptoms may include burning, tingling, or discomfort before sores appear.
-
This condition can recur over time, especially during periods of stress or weakened immunity.
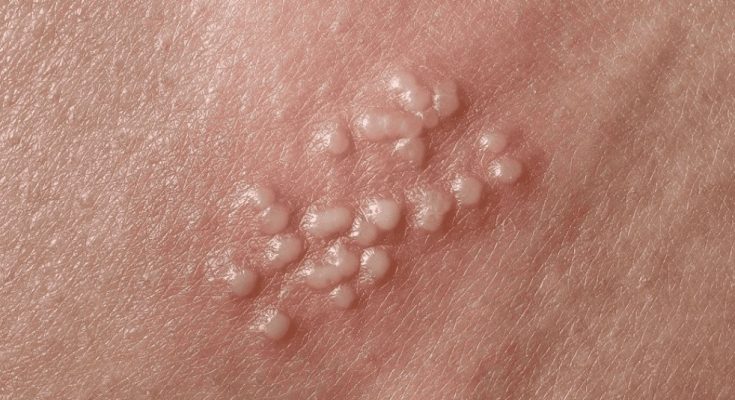
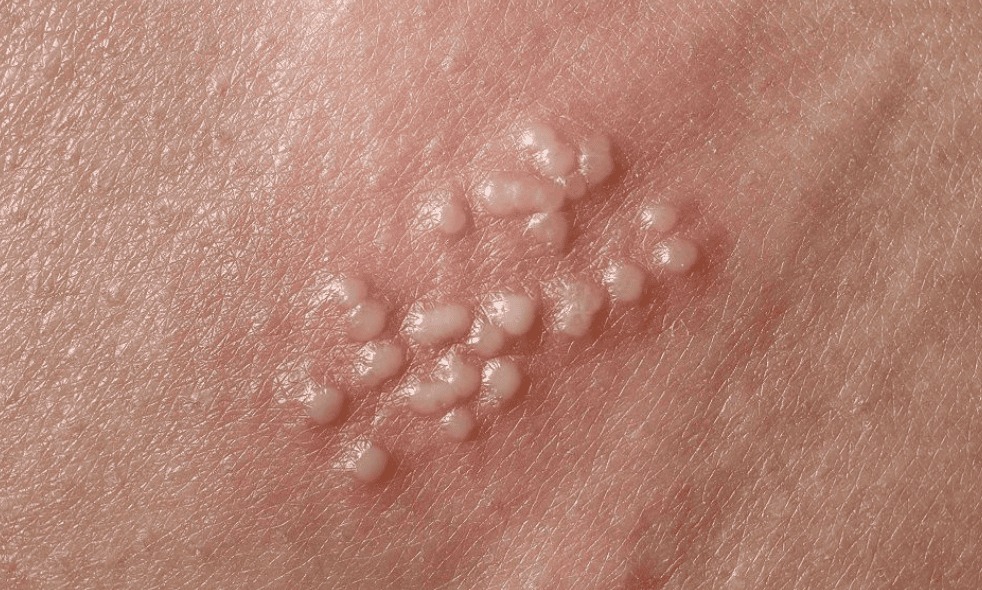
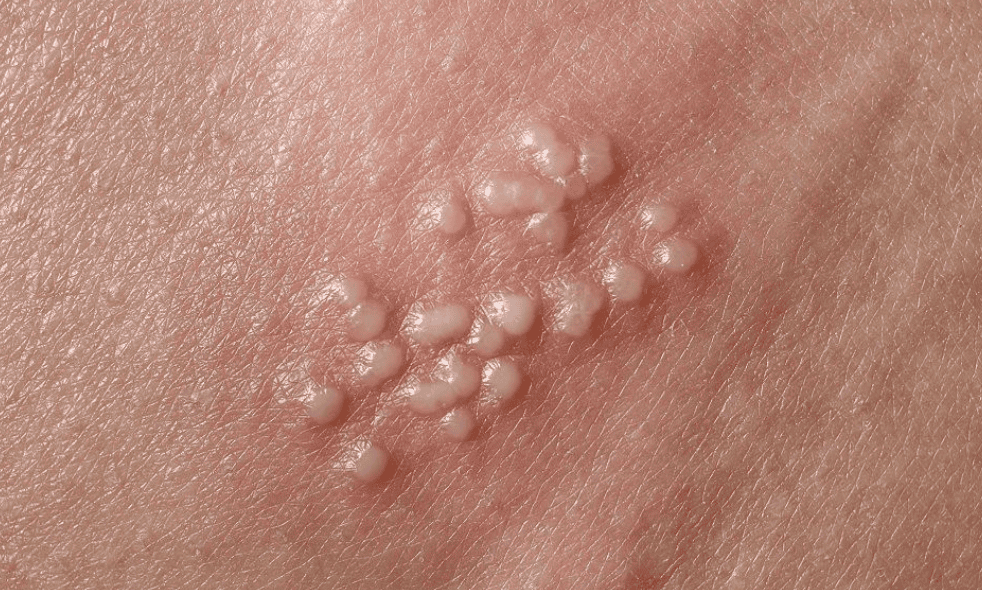
Molluscum Contagiosum
-
A skin condition caused by a virus, spreading through skin-to-skin contact.
-
Characterized by small, dome-shaped bumps with a central dimple.
-
Common in both adults and children and usually resolves on its own over time.
Syphilis
-
A bacterial infection that starts with a painless sore (called a chancre).
-
Left untreated, it can progress to more serious stages affecting internal organs.
-
Early detection and antibiotic treatment are highly effective.
Lichen Sclerosus / Lichen Planus
-
These are chronic inflammatory skin conditions.
-
Can cause itchy, white patches or flat purple bumps in the genital area.
-
Best managed with medical evaluation and prescribed topical treatments.
When Should You See a Doctor?

While it’s natural to feel shy about discussing genital symptoms, early medical attention ensures peace of mind and better health outcomes. You should consult a healthcare provider if you notice:
-
Bumps or lesions that persist, grow, or become painful
-
Unusual discharge, foul odor, or bleeding
-
A sudden outbreak of multiple spots or sores
-
Accompanying symptoms such as fever or fatigue
-
New skin growths after unprotected sexual contact
Final Thoughts: Don’t Self-Diagnose—Get Answers
Skin changes in the genital area can result from a wide variety of causes, and many are treatable once properly diagnosed. But because symptoms can overlap between minor and serious conditions, self-diagnosis is risky.
If you’re unsure about what you’re experiencing, prioritize hygiene, avoid irritation, and seek professional medical guidance. A short visit to your doctor can provide clarity, relieve stress, and set you on the right course for treatment or prevention.
Sources:
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – STIs Overview
-
Mayo Clinic – Common Causes of Genital Skin Changes